There are two tasks in Academic Writing test. Task 1 and Task 2. In Academic IELTS Writing Task 1, all candidates are asked to describe information presented in a graph, table, chart or diagram etc. and to present the description in their own words. Candidates are required to write at least 150 words in task 1. Writing Task 2 requires the candidates to formulate and develop a position in relation to a given prompt in the form of a question or statement. Ideas should be supported by evidence, and examples may be drawn from the candidates’ own experience. Responses must be at least 250 words in length.....
IELTS Writing Preparation: Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 Preparation:
Things you should know about Academic Writing Task 1:
• You are asked to describe information presented in graph/ table/ chart/ diagram.
• You have 20 minutes to finish the task and you have to write at least 150 words.
• If you are asked to use the information presented in the graph you must be careful not to copy it.
In Academic Writing task 1, candidates are assessed on their ability to:
• Organise, present and possibly compare data.
• Describe the stages of a process or procedure.
• Describe an object or event or sequence of events.
• Explain how something works.
Introduction + Basic/General Trends + Details Description + Conclusion/Summary (Optional).
The IELTS Academic writing task 1 requires several vocabularies. Each of these parts has a specific format and therefore being equipped with the necessary vocabulary will help you to write the task 1 efficiently and will save a great deal of time. Before you go through the details of how to write Academic Writing task 1, you must learn the necessary vocabulary and words first to write a better answer.
Well, now you know the structure and vocabulary for the Academic Writing Task 1. Continue ahead...
Four steps should be followed to write a better Academic writing task 1:
1. What type of presentation it is and what it is asking.
2. Collecting data/information.
3. Planning for writing.
4. Representing in an organised form.
First Step: Analise.
Analise the question first .Look whether it is a diagram / table /figure / illustration / graph / figure / chart / flow chart or a picture. Now look what the question is asking to do. For example, the question might ask to compare, contrast, analyse, summarise or more than one thing.
Second Step: Collecting data/information.
You must collect/ understand the following data and information from the figure.
a) Time: Be sure whether the time presented in the graph/ figure are present/ past/ future or a mixture of these three. Your writing has to be in the correct Tense according to the time presented.
b) Theme: Be sure what the figure/ diagram/ picture is trying to represent.
c) Place and Position: About what place or field the data are all about?
d) Main Point: What's the central idea of the presented graph/ diagram?
e) General Trend: Figure out the General Trend(s).
f) Effects & Result: Find out the effects and results.
g) Conclusion: Plan what you should include in the conclusion.
Example:
You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
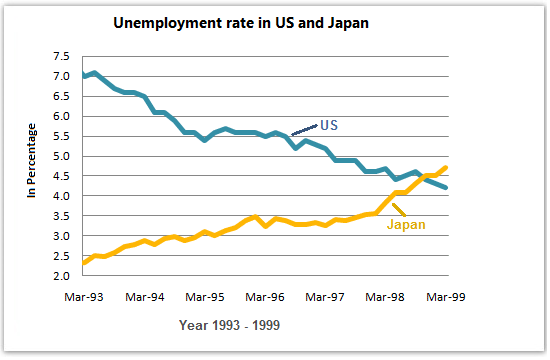
The graph below shows the unemployment rates in the USA and Japan between March 1993 and March 1999. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
You should write at least 150 words.
First Step (worked out): Analise:
It is a line graph with 2 lines. The graph is asking to summarise the main features of the unemployment rate.
Second Step (worked out): Collecting data/information:
Time: From March 1993 to March 1999.
Theme: Unemployment rates of USA and Japan.
Place and Position: USA and Japan.
Main Point: The unemployment rate has decreased in the USA and has increased in Japan.
General Trend: Initially unemployment rate was higher in the USA than Japan but over the period the USA managed to reduce the rate and in case of Japan the reverse was true.
Effects & Result: Effects: unknown. Result: as General Trends.
Conclusion: Unemployment rate was higher in the USA than Japan but over the period the USA managed to reduce the rate and in case of Japan the reverse was true.
Third Step: Essay Planning:
You should make a plan after you are done with the first 2 steps. This step involves the following orders.
a) Writing a balanced Introduction.
b) Writing a general trend
c) Detailed description of the figure and supporting the description.
d) Describing the results.
e) Writing the conclusion.
How to write a balanced introduction:
The introduction part of a writing is very important hence it reflects your skill of writing. Readers decide whether to read further or completely avoid the whole writing after reading the introduction. So in every writing introduction part should be very organised. In case of IELTS academic writing task 1, you should use the following structure and vocabularies to write a balanced introduction.
What it is (table/ graph/ chart/ diagram/ picture/ flow chart) + What it does (presents data/ shows comparison/ summarize / contrast/ give projection or prediction) + What about (in this case the unemployment rate) + Place (in this case US and Japan) + Time (in this case 1993 to 1999) + Presentation of X and Y axis (here X axis represents time and Y axis represent percentage of work force) + Other relevant information.
Example: The provided line graph provides information on unemployment rates in USA and Japan from March 1993 to March 1999. Here the bold line represents the unemployment rate of Japan and the dotted line for the USA. In the provided line graph the X axis shows time with one-year interval and the Y axis represents unemployment rate.
How to write a better general trend:
The general trend part should be immediately after the introduction part. It is recommended to write the general trend parts in the same paragraph with the introduction. The general trend part should focus the main point of the presentation and should not be too large with lots of information. However you should not give the specific figure, time, amount or data presented in the graph, rather try to use daily life English to make the main reader interested about the whole writing. You can use phrases like As is presented/ as is observed / in general / in common etc. to start this part.
Example: As is observed from the graph, initially in 1993 the unemployment rate in the USA was significantly higher than that of Japan. But over the 6 years, the USA managed to reduce this rate and the reverse was true for Japan where unemployment rate increased in these 6 years.
How to write an attractive details description:
The Detailed description part comes after the introduction and general trend and should be written in the second paragraph. In this part, you should describe the graph / table / chart / diagram etc. While describing, keep in mind that, you are not expected to write down all the data provided in the question, rather your ability to describe the presentation in general English.
» Use appropriate tense to describe the data.
» Use transitional words like, besides, as well as, likewise, in addition, additionally, again, on the other hand etc. to make your sentences relevant and coherent.
» Try to mention the initial, highest, lowest and projection points.
Things you should avoid in this part:
» Do not describe all the data and facts presented in the graph.
» Don't include your own opinion, imagination or solution.
» DO NOT use contractions (can not=can't, do not =don't etc, will not=won't) in your writing.
How to describe the results:
If you want to and really need to describe the result of the graph, then write it at the end of the detailed description. However, if results-writing makes something repeated ( those that has already been described), then you do not need to write the result apparently.
Example: The USA managed to decline their unemployment rate from 7% to almost 5% in 6 years but on the other hand the rate has increased in Japan from only 2.5% to approximately 5%.
How to write a good and efficient conclusion:
The conclusion is an important part of the whole writing and that is why you must be careful to write a better conclusion. The conclusion part of the Academic IELTS writing 1 is also knows as summarising. So write down the main point/theme of the graph in short. You should never include your own point of view, personal opinion or suggestion to solve a problem in conclusion. In some cases of Academic IELTS writing task 1, it optional to write the conclusion, hence the data are already described and summarised before the conclusion. However, if you need to write the conclusion part, use one of the following words to start the sentence:
In conclusion / in short / to conclude / to sum up / in brief / in summary etc.
Example: It conclusion, the unemployment rate in the USA decreased in 6 years and the opposite scenario was true for the Japan.
Academic IELTS Writing Task 1 Preparation (Part 2)
Writing Task 1 (Academic)
Practice 1:
» You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
The graphs below show the numbers of male and female workers in 1975 and 1995 in several employment sectors of the republic of Freedonia.
Write a report for a university teacher describing the information shown.
» You should write at least 150 words.


First Step- Analyse:
Two line graphs given in the question. These graphs should be described by comparing/ contrasting main features and should be presented as a report to a University Lecturer.
Second Step- Collecting data/information:
a) Time: First graph is for 1975 and the second one is for the year 1995.
b) Theme: Comparison of men and women workers in 6 Employment sectors.
c) Place and Position: Freedonia.
d) Main Point: Comparison of men and women employees in respect to the job sectors.
e) General Trend: Initially in 1975, Men employees occupied most of the jobs in all sectors.
» You should write at least 150 words.


First Step- Analyse:
Two line graphs given in the question. These graphs should be described by comparing/ contrasting main features and should be presented as a report to a University Lecturer.
Second Step- Collecting data/information:
a) Time: First graph is for 1975 and the second one is for the year 1995.
b) Theme: Comparison of men and women workers in 6 Employment sectors.
c) Place and Position: Freedonia.
d) Main Point: Comparison of men and women employees in respect to the job sectors.
e) General Trend: Initially in 1975, Men employees occupied most of the jobs in all sectors.
f) Effects & Result: The number of women employees increased significantly, especially in communication sectors over the 20 years period.
g) Conclusion/ Summary: Conclusion should be a summary of theme, general trend, and result. Sometimes you do not need to write the conclusion part. Keep in mind that graph writing conclusion is not same as writing the conclusion for an essay.
Third Step- Report Planning:
A) Writing Introduction:
The provided graphs represent information about the male and female workers of Freedonia in six different sectors in 1975 and 1995.
B) Writing General Trend:
As is observed from the two given graphs, the number of male employees was larger in all sectors of employment than that of women but after 20 years this discrimination had plummeted, in particular, in banking & finance sector and surprisingly more women were employed in communication sector in 1995 than their counterpart -men.
C) Writing Detailed Description:
According to the illustration, almost 600 men out of the thousand workers were employed in manufacturing jobs in 1975 and that was almost twice than the number of women employed in the same sector. After 20 years in 1995, the number of male workers in this sector increased to around 700/thousand but the number of women workers remained almost the same as it was in 1975. Again, male workers in banking, wholesale & retail trade, defense, public sectors were significantly larger in number than female workers in 1975. The highest number of workers, both the men and women, worked in public sectors in 1975. In this year in public sectors, almost 80 per thousand were men and 650 per thousand were female, which was larger in number than any other sectors. Job sectors like defense were mostly occupied by men whereas women were very small in number in this sector. In the year 1975, the smallest gap between the number of male and female workers could be observed in the communication sector. After 20 years, in 1995 the scenario changed remarkably. In this year female went ahead of men in communication and trade (wholesale & trade) sectors. Also the different of male and female employees in banking and finance became ignorable. On the other hand, the number of male employees had declined in defense and the opposite is true for women. The job condition in manufacturing sectors remained almost the same as it was 20 years earlier.
D) Describing the results:
Not necessary as it has already been described in detail description.
E) Writing the summary/ conclusion:
In summary, it can be clearly observed from the given graphs that, female participation in different job sectors had significantly improved and in some sectors, they went ahead of men.
Tips 1: Many teachers will tell you not to write any conclusion or summary in your graph answer. Here is what we think-
» Do not write a separate conclusion or summary if you have already described the general trends clearly in the introduction part and have already written more than 150 words.
» In case you find that you are yet to write 150 words and have something to say about the overall graph, go for the conclusion/ summary part.
Tips 2: You should use as many transitional words as appropriate to make the writing coherent. Do not copy the sentences from the given question. You are expected to write a summary, so you should never write down all the facts and figures presented in the graph. Never write less than 150 words.
IELTS Writing Task 1 (Academic )
Practice 2:
» You should spend about 20 minutes on this task.
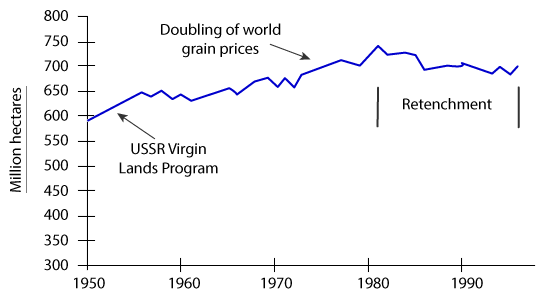
The graph below shows the area of land from which grain was harvested.
Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information in the graph.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
» You should write at least 150 words.
World grain harvested area, 1950 – 96
First Step- Analyse :
The given presentation is a line graph. Here 'X' axis represents the time and 'Y' axis represents the area in million hectares where grain was harvested. The question is asking to summarise the main features and to make comparisons where relevant.
Second Step- Collecting data/ information:
a) Time: Past (1950 to 1996).
b) Theme: Total land in million of hectares where grains were harvested.
c) Place and Position: All around the world.
d) Main Point: World grain harvested area.
e) General Trend: Amount of land increased from1950 to 1980 and then this amount decreased.
f) Effects & Result: Virgin land program, Doubling the price of grain, Retrenchment.
g) Conclusion: Not necessary.
Third Step- Report Planning:
A) Writing Introduction:
The given line graph shows the total grain harvested area around the world in million of hectares from 1950 to 1996 and the reasons why the amount changed. Here the 'X' axis represents time and the 'Y' axis shows the land area in million of hectares.
B) Writing General Trend:
As is observed from the graphs, total grain harvested area increased until 1980, at which point there was a reduction due to retrenchment.
C) Writing Detailed Description:
According to the given illustration,
D) Describing the results
Not necessary as it has already been described in detail description.
E) Writing the conclusion
Not necessary.
Tips: You should use transitional words to make the writing coherent. Do not copy the sentences from the given question. You are expected to write a summary, so you should never write down all the facts and figures presented in the graph. Never write less than 150 words and any report writing in Academic IELTS task 1 which is less than 150 words, would lose points.
Familiarity with these words would be useful in all IELTS Writing test modules. Common connective words are:
Addition: in addition, and, similarly, likewise, as well as, besides, furthermore, also, moreover, and, then, too, not only ... but, even besides, this, that etc.
Sequence: first(ly), initially, second(ly), to begin with, then, next, earlier/later, after this/that, following this/that, after wards etc.
Consequence: as a result, thus, so, therefore, consequently, it follows that, thereby, eventually, then, in that case, admittedly etc.
Certainty: obviously, certainly, plainly, of course, undoubtedly etc.
Condition: if, unless, whether, provided that, for, so that, depending on, only if, providing that etc.
Definition: is refers to, means, that is, consists of etc.
Summary: in conclusion, in summary, lastly, finally, to sum up, to conclude, to recapitulate, in short etc.
Example: for instance, one example, for example, just as, in particular, such as, namely, to illustrate etc.
Reason: since, as, so, because (of), due to, owing to, the reason, why, in other words, leads to cause etc.
Time: before, since, as, until, meanwhile, at the moment, when, whenever, as soon as, just as etc.
No comments:
Post a Comment